主要是对于递归的理解没有很透彻
二叉搜索树
二叉搜索树(Binary Search Tree, BST)是一种很常见的二叉树。它的定义是: 一个二叉树中任意节点的值要大于等于所有左子树节点的值,且要小于等于右边子树所有节点的值
100. 相同的树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| class Solution {
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(p == null && q == null) return true;
else if(p == null ^ q == null) return false;
else if(p.val != q.val) return false;
else {
return isSameTree(q.left, p.left) &&
isSameTree(q.right, p.right);
}
}
}
|
方法二:
广度优先搜索
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| class Solution {
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(p == null && q == null) return true;
else if(p == null || q == null) return false;
Queue<TreeNode> queue1 = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue2 = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue1.offer(p);
queue2.offer(q);
while(!queue1.isEmpty() && !queue2.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node1 = queue1.poll();
TreeNode node2 = queue2.poll();
if(node1.val != node2.val) return false;
TreeNode left1 = node1.left, right1 = node1.right,left2 = node2.left, right2 = node2.right;
if(left1 == null ^ left2 == null) return false;
if(right1 == null ^ right2 == null) return false;
if(left1 != null) queue1.offer(left1);
if(right1 != null) queue1.offer(right1);
if(left2 != null) queue2.offer(left2);
if(right2 != null) queue2.offer(right2);
}
return queue1.isEmpty() && queue2.isEmpty();
}
}
|
判定是否一个二叉树中任意节点的值要大于等于所有左子树节点的值,且小于等于右边子树所有节点的值
1
2
3
4
5
6
| public boolean isValidBST(Node root){
if (root == null) return true;
else if (root.l != null && root.val <= root.l.val) return false;
else if (root.r != null && root.val >= root.r.val) return false;
return isValidBST(root.l) && isValidBST(root.r);
}
|
但是这个算法出现了一定的错误,BST的每一个节点应该要小于右边子数的所有节点,下面这个二叉树显然不是BST,但是上述算法会将其判定为BST
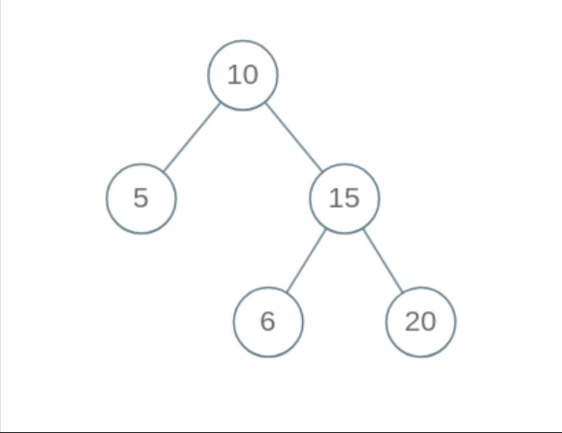
重新看一下BST的定义,Root做的并不只是和左右节点的比较,而是需要和整个左子树和右子树的所有节点进行比较。这种情况下我们可以使用辅助函数,增加函数参数列表。在参数中携带额外信息。
1
2
3
4
5
6
| boolean isValid_BST(Node root, Node min, Node max){
if (root == null) return true;
if (min != null && root.val <= min.val) return false;
if(max != null && root.val >= max.val) return false;
return isValid_BST(root.left, min, root) && isValid_BST(root.right, root, max);
}
|
98. 验证二叉搜索树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
根据二叉树的性质,在递归调用左子树时候,将上界改为root
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| class Solution {
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
return judge(root, Long.MAX_VALUE, Long.MIN_VALUE);
}
public boolean judge(TreeNode root, long max, long min){
if(root == null) return true;
if(root.val >= max || root.val <= min) return false;
return judge(root.left, root.val, min) && judge(root.right, max, root.val);
}
}
|
一:在BST中查找一个数字是否存在
根据我们的指导思想,我们可以这样写
1
2
3
4
5
| public boolean isInBST(TreeNode root, int target){
if(root == null) return false;
if(root.val == target) return true;
return isInBST(root.left, target)|| isInBST(root.right, target);
}
|
这样写完全正确但是如何将BST“左小右大”的特性运用上?
很简单,其实不需要这样递归的左右两边搜索,类似于二分查找的思想,根据target和root.val的大小进行比较,就能排除一边。我们将上面的思路稍稍改动一下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| boolean isInBST(TreeNode root, int target){
if(root == null) return false;
if(root.val == target) return true;
if(root.val < target) return isInBST(root.right, target);
if(root.val > target) return isInBST(root.left, target);
}
|
700. 二叉搜索树中的搜索 - 力扣(LeetCode)
1
2
3
4
5
6
| class Solution {
public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int tar) {
if(root == null || root.val == tar) return root;
return root.val > tar? searchBST(root.left, tar) : searchBST(root.right, tar);
}
}
|
二、在BST中插入一个数字
对于数据结构的操作无非是遍历+访问,遍历就是“找”,访问就是“改”。具体到这个问题,插入一个数字,就是先找到插入位置,然后进行插入操作。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val){
if(root == null) return new TreeNode(val);
if(root.val < val) root.right = insertIntoBST(root.right, val);
if(root.val > val) root.left = insertIntoBST(root.left, val);
return root;
}
|
701. 二叉搜索树中的插入操作 - 力扣(LeetCode)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| class Solution {
public TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if(root == null) return new TreeNode(val);
else if(root.val < val) root.right = insertIntoBST(root.right,val);
else if(root.val > val) root.left = insertIntoBST(root.left,val);
return root;
}
}
|
三、在BST中删除一个数字
这个问题有一点复杂,跟插入的操作优点类似,先找然后再改。先将框架写出来
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key){
if(root.val == key){
}else if(root.val > key){
root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key);
}else if(root.val < key){
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key);
}
return root;
}
|
找到了这个节点,比方说是节点A,如何将这个节点进行删除,这是难点。因为删除节点的同时不能破环BST的性质。有三种情况,这里使用图片进行说明。
情况一:恰好是末端节点,两个子节点都为空,那么它可以当场去世了。
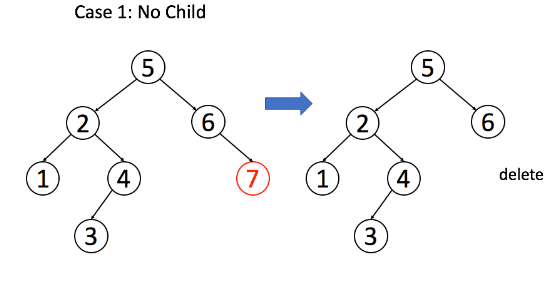
1
| if(root.left == null && root.right == null) return null;
|
情况二:A只有一个孩子节点,那么就让它的孩子节点接他的班
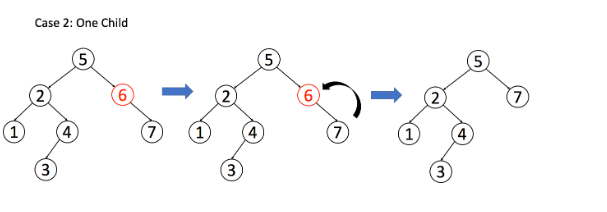
1
2
3
|
if(root.left == null) return root.right;
if(root.right == null) return root.left;
|
情况三:A具有两个子节点,为了不破环BST的性质,A必须找到左子树中最大的那一个节点或者右子树中最小的那一个节点来接替自己。
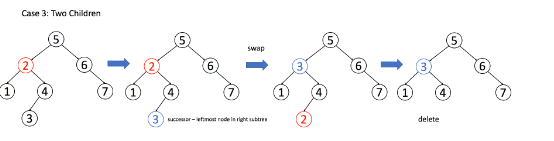
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| if(root.left != null && root.right != null){
TreeNode minNode = getMin(root.right);
root.val = minNode.val;
root.right = delete(root.right, minNode.val);
}
|
三种情况分析完毕,填入框架,简化一下代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key){
if(root == null) return null;
if(root.val == key) {
if(root.left == null) return root.right;
if(root.right == null) return root.left;
TreeNode minNode = getMin(root.right);
root.val = minNode.val;
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, minNode.val);
}else if(root.val > key){
root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key);
}else if(root.val < key){
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key);
}
return root;
}
TreeNode getMin(TreeNode node){
while(node.left != null) node = node.left;
return node;
}
|
450. 删除二叉搜索树中的节点 - 力扣(LeetCode)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| class Solution {
public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
if(root == null) return root;
if(root.val == key){
if(root.left == null && root.right == null) return null;
if(root.left == null) return root.right;
if(root.right == null) return root.left;
else{
TreeNode min_Node = getMin(root.right);
root.val = min_Node.val;
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, min_Node.val);
}
}
else if(root.val > key){
root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key);
}else if(root.val < key){
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key);
}
return root;
}
public TreeNode getMin(TreeNode root) {
while (root.left != null)
root = root.left;
return root;
}
}
|



